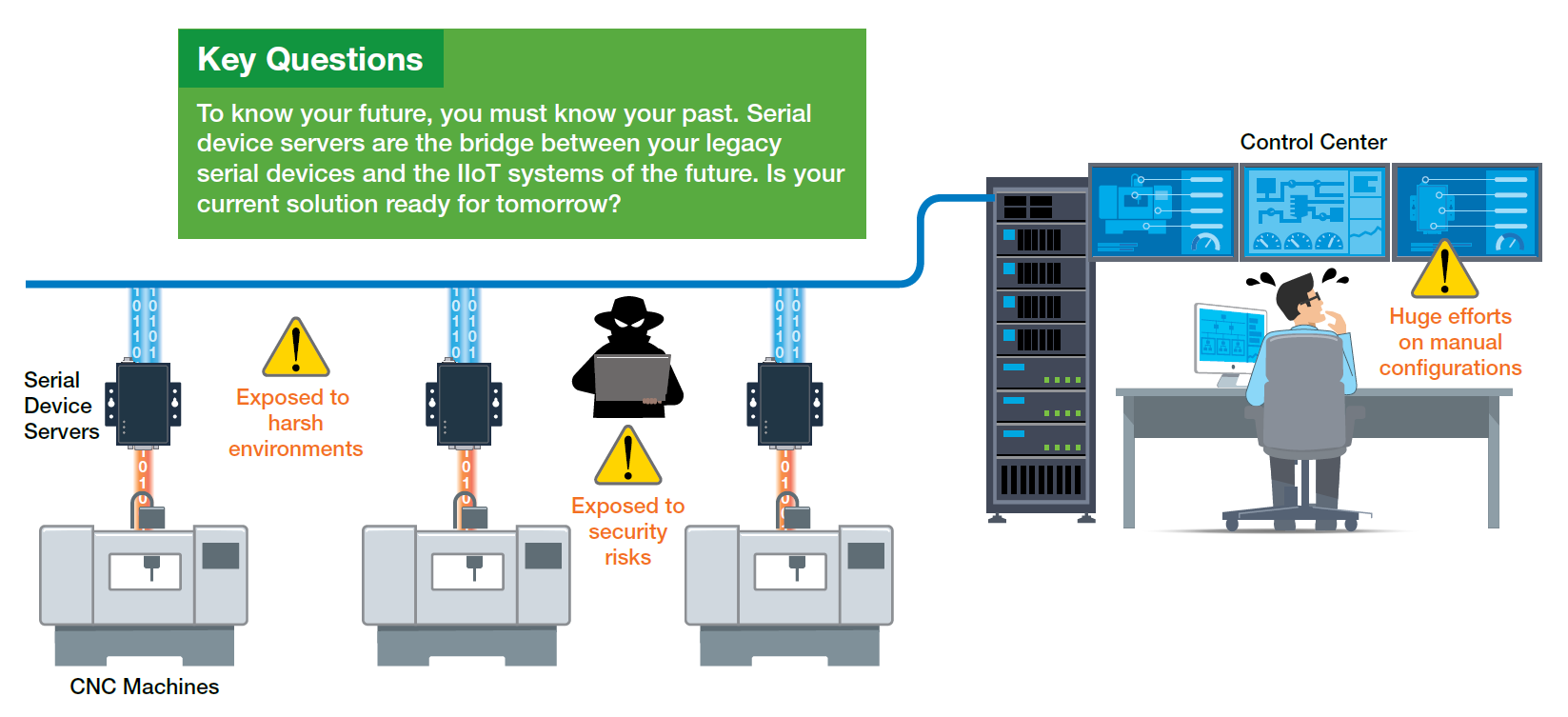
There is no need to say goodbye to all your loyal legacy devices in order to transform your existing industrial automation system into a modern IIoT application. Even though the legacy devices in your industrial edge systems may be older than most mobile phones or laptops in use today, they continue to fulfill a valuable purpose and are oftentimes too costly to replace altogether.
However, IIoT applications often take advantage of supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems that use the Internet Protocol (IP) to communicate over Ethernet networks. Your legacy devices, on the other hand, most likely use serial-based communications with fieldbus protocols, which are very different from IP communications. So how do you connect legacy serial devices with Ethernet-based SCADA systems when they cannot talk to each other?
Replacing all of your legacy serial devices with newer Ethernet-based devices would clearly solve the communication problem. But upgrading all of your equipment would also be costly and disruptive. For example, replacing a serial-based CNC machine is extremely expensive and would take a huge chunk out of the budget of most businesses. Besides, serial devices have their own benefits. For example, RS-485 power meters can perform multidrop communication, which makes wiring easy and efficient. Adding serial-to-Ethernet solutions between your serial devices and IP-based systems can help you save costs and effort, and also allow you to enjoy both the simplicity of serial communications and the advantages of Ethernet. In this article, we will show you how to choose a serial-to-Ethernet solution that works best for you.
Key Criteria for Choosing Serial Device Servers
If you need to connect proprietary serial devices over IP networks, serial device servers can provide a simple bridge between your legacy serial devices and modern communication systems. However, without sufficient knowledge of how serial device servers work, you could end up spending unnecessary time and effort. Here are three key criteria you should remember when choosing a serial device server. If your legacy serial devices speak in standard fieldbus protocols, such as Modbus and PROFIBUS, read our article to learn how to choose the right protocol gateway to enable IP communications.

Make Every Step Count
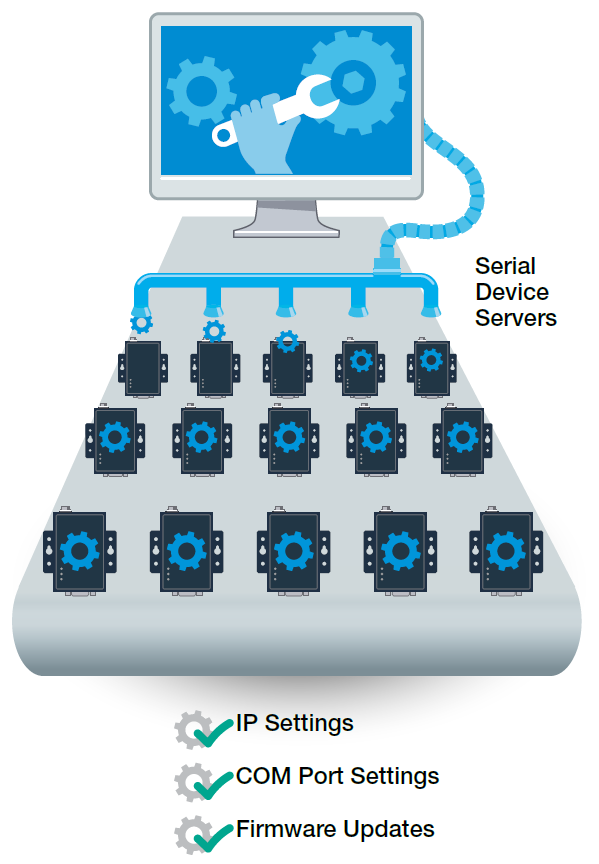
Compared to completely replacing all your hardworking legacy devices, learning how to use and deploy serial device servers can be a breeze. However, enabling dozens of serial device servers could also take a great deal of time and effort to manually configure countless settings. Whether you are configuring IP addresses for each of your serial device servers, setting up virtual serial (COM) ports, or updating serial and Ethernet parameters, serial device server configurations can be painful if you don’t have clear instructions or a smart utility to help walk you through all the steps. The frustration can even extend into the operations phase when you need to manage or maintain dozens of devices.

When choosing a serial device server, check if there is an easy-to-use web console or utility to simplify configuration and management. Don’t overlook this feature because there will only be more field devices that need to be connected as your network matures. Repeating configuration processes increases the burden of device management and can really wear you down.

Protecting Your Networks in a Connected World
In the past, industrial automation only required connecting a limited number of field devices within a small, independent, and private network. In the era of the IIoT, however, industrial applications now require more field devices to be connected over public networks that allow both OT and IT engineers to access field data. Increasing the accessibility of your field devices with the outside world offers innumerable benefits but also exposes your networks to new security risks. Without proper protection, your applications can be extremely vulnerable. For example, traffic contorllers can be targeted by hackers who want to mess with traffic signals to cause havoc on our road. Watch our video to learn how you can block unwanted access.
People can access your application through countless entry points, including your serial device servers. Be sure the serial device server you choose has sufficient security functions to keep your data protected. Using strong login passwords or creating a whitelist are the simplest ways to limit access to your serial device servers to authorized personnel. Closing unused ports on serial device servers can also be an efficient way to block unnecessary entrances that could be exploited. During data transmissions, using a secure protocol, such as HTTPS, can also minimize unwanted access to your field data.

Don’t Forget the First “I” in “IIoT”
Are you still using commercial-grade serial device servers for your industrial applications? Commercial serial device servers may seem adequate if you have been using them for a while or only need to connect a few field devices. But when it comes to IIoT projects that require connecting a large number of field devices and transmitting critical field data on time, you should reconsider. Choosing a serial device server that is capable of enduring harsh environments, such as extreme temperatures or high electromagnetic interference, can minimize the chances of data loss arising from a serial device server shutdown.

Using the above three criteria to evaluate your serial device server options can help you find the right solution for your industrial applications. For example, Moxa’s NPort serial device servers are developed with easy-to-use, secure, and reliable features that are ideal for connecting field devices in IIoT applications. If you are interested in learning more about industrial connectivity, download our E-book.