In order to unlock valuable information from collected data and attain centralized management in control rooms, many businesses are upgrading their existing systems to IP-based networks and connecting their devices and applications, such as video surveillance, to the Internet. However, in the age of the IIoT, simplifying network deployments and upgrades has become a big challenge for engineers. Furthermore, system upgrades usually require huge investments in new cables. As an alternative to investing in new cables, industrial Ethernet extenders allow users to extend Ethernet networks over 100 meters via 2-wire copper cables to fulfill various project requirements, especially for long-distance communication. In this article, we discuss four scenarios where Ethernet extenders benefit operational efficiency.
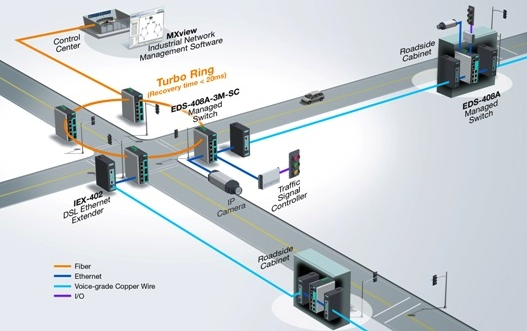
Scenario 1: Ensuring minimal interruptions to users
In the transportation industry, for example, traffic administrators often need to upgrade traffic control systems to transmit data to an operational control center. At the same time, they need to minimize possible interferences, such as roadwork and construction, on "road users," a category which includes both the pedestrians and vehicle occupants on the road. System upgrades often go hand in hand with the integration of video surveillance, calling for a larger bandwidth as a critical requirement. Industrial Ethernet extenders support point-to-point transmission over long distances through existing copper-wire infrastructures and plug-and-play configuration, which speeds up and eases network deployment. Ethernet extenders also support higher rates of data transmission, making them suitable for bandwidth-hungry applications.
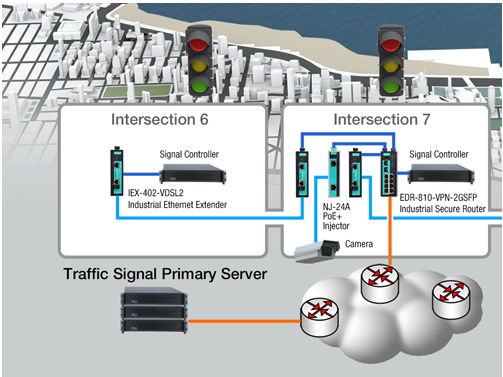
Scenario 2: Dealing with specific cabling in an application’s environment
In hazardous environments, typical in industries such as oil & gas and mining, optical fiber cabling is not an ideal option for networks because the cables are prone to damage or pose risks due to cable splicing during cable extensions. In addition, industry-specific cables are normally deployed in harsh environments. For projects that involve industry-specific cables, industrial Ethernet extenders enable users to easily build or extend a network between a control center and a harsh environment field site, where the conditions necessitate faster deployment and the ability to remotely monitor and manage devices. An industrial Ethernet extender that supports a bypass function and remote management significantly improves system reliability in mission-critical applications. For example, an oil company in Australia used industrial Ethernet extenders to successfully build a subsea oil and gas control application.
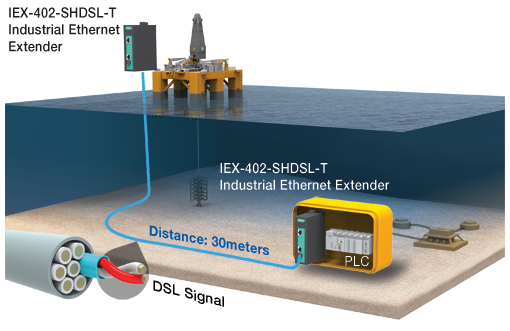
Scenario 3: Upgrading to a Larger Bandwidth Network
If an infrastructure of 2-wire copper cables already exists, and you want to upgrade your legacy system so that more devices and subsystems can connect to it, then industrial Ethernet extenders are your answer. They allow you to upgrade the system easily and quickly on the existing infrastructure. For example, a hospital in Hong Kong set up an IP-based emergency alert system in a ward, connecting it to the facility’s advanced emergency network. As the hospital was already using 2-wire copper cables for communications in their legacy systems, industrial Ethernet extenders were the perfect fit to build the new emergency alert system.
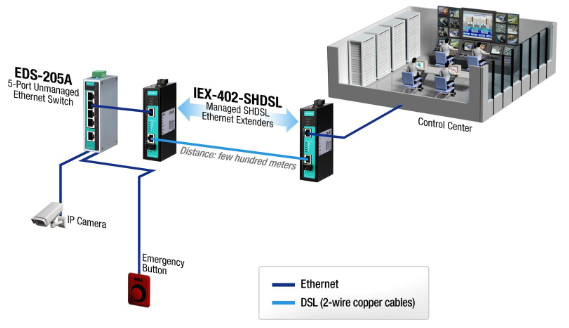
Scenario 4: The legacy system needs to be upgraded to an IP-based network, but the budget is tight
The IIoT has driven business to transform their legacy systems to IP-based networks so that everything can be connected and managed over the Internet. However, engineers also have to deal with budget constraints. To reduce cost, the ideal option is to use industrial Ethernet extenders. For example, traffic administrators recently upgraded to IP-based traffic signal systems at intersections with a CCTV surveillance system integrated over the same network. However, it wasn’t practical to lay Ethernet cables from intersection to intersection because of cost constraints and the long distances between intersections. Consequently, network engineers decided to re-use the 2-wire copper cables already installed and extend their reach from one to two kilometers between intersections by deploying industrial Ethernet extenders.